By John Erath President Donald Trump has stated that he would like to commence talks with Russia and China aimed at reducing numbers of nuclear weapons. This is an encouraging proposal; the world would undoubtedly be safer with fewer, not more, nuclear weapons. It is also much easier said than done. Arms control diplomacy is […]
Fact Sheet: Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA)
The Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA), enacted in 1990, provides financial compensation to individuals who suffered specific health conditions due to radiation exposure. This exposure resulted from atmospheric nuclear testing or employment in the nuclear weapons production industry during the Cold War. Since its inception, the program has awarded more than $2.5 billion to more than 39,000 claimants across the […]
Final Summary: Fiscal Year 2025 National Defense Authorization Act (H.R. 5009)
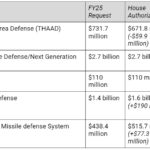
Updated December 18, 2024 Table numbers in parentheses are increases or decreases from the FY25 Request FY25 requested levels come from the Center for Arms Control and Non-Proliferation’s Fiscal Year 2025 Defense Budget Request Briefing Book Numbers may not add due to rounding Total National Defense Discretionary Spending Request (050) DOD Nuclear Weapons Funding Request […]
Comparative Summary: Fiscal Year 2025 National Defense Authorization Act
Table numbers in parentheses are increases or decreases from the FY24 Request FY25 requested levels come from the Center for Arms Control and Non-Proliferation’s Fiscal Year 2025 Defense Budget Request Briefing Book Numbers may not add due to rounding Total National Defense Discretionary Spending Request (050) DOD Nuclear Weapons Funding Request for Select Programs National […]
Summary: Fiscal Year 2025 National Defense Authorization Act (S. 4638) as passed by the Senate Committee on Armed Services
Table numbers in parentheses are increases or decreases from the FY25 Request FY25 requested levels come from the Center for Arms Control and Non-Proliferation’s Fiscal Year 2025 Defense Budget Request Briefing Book Numbers may not add due to rounding Total National Defense Discretionary Spending Request (050) DOD Nuclear Weapons Funding Request for Select Programs National […]