Updated May 2023
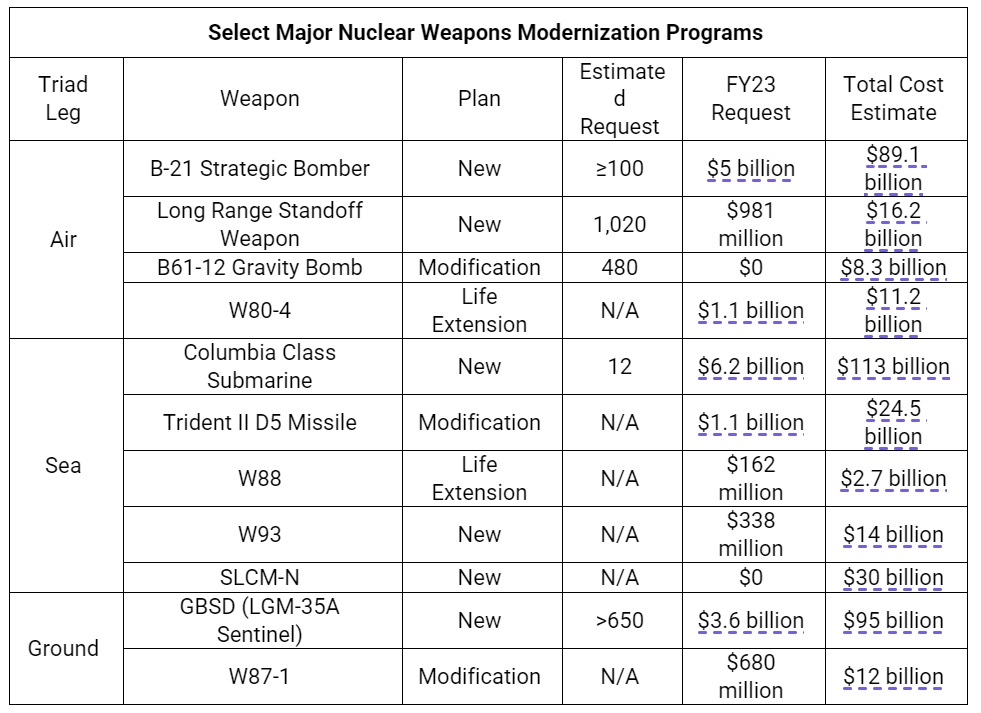
The United States plans to spend up to $1.5 trillion over 30 years to overhaul its nuclear arsenal by rebuilding each leg of the nuclear triad and its accompanying infrastructure. The plans include, but are not limited to, a new class of ballistic missile submarines, a new set of silo-based intercontinental ballistic missiles, a new nuclear cruise missile, a modified gravity bomb, a new stealthy long-range strike bomber, and accompanying warheads (with modified or new warhead pits) for each delivery system.
Annual Costs
The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) plans to spend $16.5 billion to maintain and update the U.S. nuclear arsenal in fiscal year 2023. This money is specifically designated for weapons activities, including modifications and life extension programs for nuclear warheads. The Pentagon will spend more than $34.4 billion this fiscal year to modernize the triad’s delivery systems, including warplanes and submarines, and their command, control, and communications systems. The most recent report from the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projects the cost of modernization to be $188 billion through 2030.
Constraints
The Government Accountability Office (GAO) has repeatedly expressed concern over the NNSA’s inability to manage the costs and schedules of modernization. For example, NNSA and the Department of Defense (DOD) acknowledged in 2022 that the first W80-4 warhead will not be produced until 2027 after an initial planned delivery date of 2025. Similarly, the W87-1 warhead is expected to begin production in 2030, but it is unclear whether the United States can produce enough plutonium cores to meet this schedule. Reporting to a House Armed Services subcommittee in March 2020, GAO argued that the NNSA should consider “potentially deferring the start of or canceling specific modernization programs” in order to bring its modernization plans into actual alignment with future budgets.
CBO also highlights that “competition for funding among acquisition programs will force difficult choices about which programs to pursue.” The push to add even more new programs to the plan, such as a nuclear sea-launched cruise missile, would add even more strain to an already stretched-thin enterprise and divert resources and focus from higher modernization priorities.